Use an OAuth API Token With an Integration
- Applies to:
- All versions
- Role required:
- Admin
Prerequisites
What You will Need
You should have recorded the following when generating your OAuth API Token:
- Key (Implemented as an OAuth 2.0 Client Id)
- Secret (Implemented as an OAuth 2.0 Client Secret)
OAuth 2.0 Authorization Flows
OAuth 2.0 authorization flows are typically used to ensure that a user of an application has allowed the application to access their data stored in a different application or service. A common example is using Facebook authentication with Spotify, granting Spotify access to your contacts so that your contacts' Spotify playlists are available to you. With Expert, an authenticated user on an Expert site (Community Member or Pro Member) can authorize an integration to access or write data over the Expert API, using their user identity and assigned permissions. There are two supported authorization flows: the Authorization Code Flow and the Device Code Flow.
Scopes
Scopes that narrow the access granted to integrated applications can be useful to provide limited access to applications that do not need to write data or perform administrative tasks. Access tokens with scopes that provide Pro Member or Administrator access will expire earlier than those that provide limited (Community Member) access (refresh tokens, explained later in this article, can retrieve a new access token without initiating the entire authorization flow).
| Scope | Description | Access Token TTL | Refresh Token TTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| profile | The integration can read and write user account data, and view private content | 24 hours | 6.5 days |
| profile seated | The integration can read and write user account data, view and publish public or private content (depending on assigned page permissions), and perform administrative tasks if the user is an administrator | 60 minutes | 24 hours |
| profile mindtouch | The integration can read account data and have additional metadata in authorization claims for site, groups, external claims, and role. This can be combined with `seated` scope for additional access. | 24 hours | 6.5 days |
Authorization Code Flow
The Authorization Code Flow is a scheme for server-hosted applications with a web browser user interface. The web application redirects a user to the Expert site to verify authentication and authorize the integration between the web application's server-side component(s) and the Expert API. The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code Flow is a common, industry-supported, authorization scheme for web applications and can be implemented with many existing third-party libraries. Read the RFC6749 for more details.
Redirect User to Authorize
The web application redirects the user to an authorization endpoint on the Expert site that will optionally (based on site configuration) prompt them with the option to sign-in and authorize the integration.
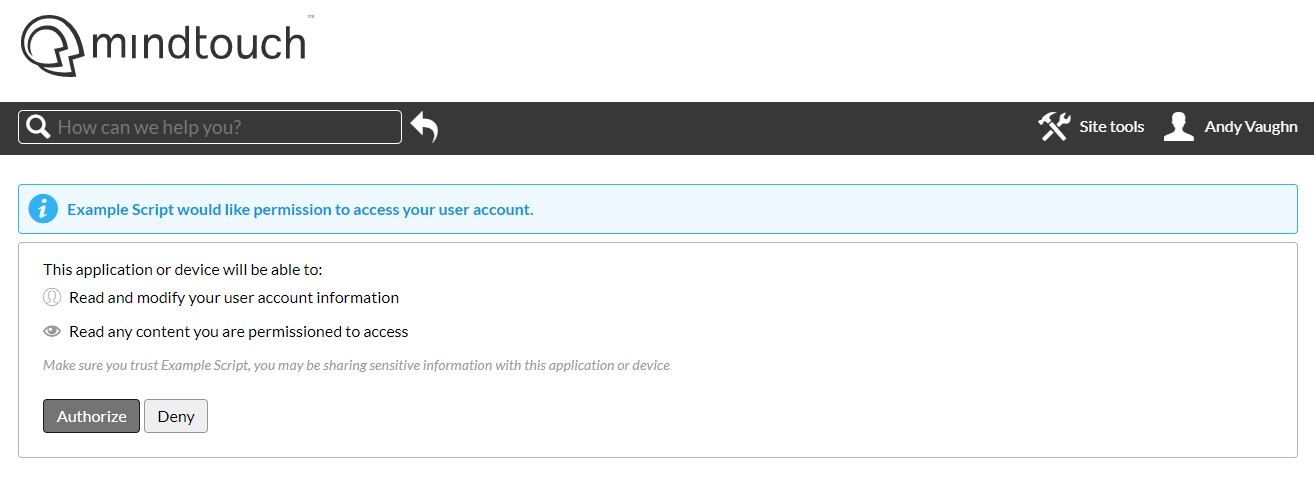
After completion, the Expert site will redirect the user back to the web application with an authorization code in the URL.
GET https://{hostname}/@app/auth/{authid}/token/authorize?client_id={key}&scope={scope}&response_type=code&prompt={prompt}&redirect_uri={redirect_uri}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {hostname} | string | The Expert site hostname |
| {authid} | int | The identity provider service to use for authentication |
| {key} | string | The OAuth API Token key |
| {scope} | string | Single space-separated scopes of the authorization request (required: profile) (allowed: profile seated) |
| {prompt} | string? | Should the user be prompted to provide consent before authorization is complete? (options: prompt, none) (NOTE: Setting this value to 'none' can be overridden by the Professional Services managed configuration of the identity provider service used to authenticate) |
| {redirect_uri} | string | The web application callback URL that will receive the authorization code after the user completes the authorization flow |
Request Access Token
The web application's server-side component(s) will send a payload to an access token endpoint on the Expert site. HTTP Basic Authorization, using the OAuth API Token key and secret as username and password, respectively, establishes trust during the access token request.
$ curl --request POST --user {key}:{secret} --data {body} https://{hostname}/@app/auth/{authid}/token/access.json
// URL encoded form payload
grant_type=authorization_code&code={code}&redirect_uri={redirect_uri}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {hostname} | string | The Expert site hostname |
| {authid} | int | The identity provider service used for authentication |
| {key} | string | The OAuth API Token key |
| {secret} | string | The OAuth API Token secret |
| {body} | application/x-www-form-urlencoded | The URL encoded access token request payload |
| {code} | string | The authorization code received in the redirect to the web application callback URL |
| {redirect_uri} | string | The web application callback URL. MUST match redirect_uri from access token request. |
The access token response is common to all authorization flows, and is described in detail later in this article.
Device Code Flow
The Device Code Flow is the scheme for integrations running on devices with no web browser user interface or keyboard, such as television set-top boxes or appliances. In this flow, the integration pauses while the user opens a browser, on their mobile device or computer, to verify authentication on the Expert site and authorize the integration. The Device Code Flow is a newer OAuth 2.0 authorization flow (~2019), as a result, there is less third-party library support than the Authorization Code Flow.
Request Device Code
The integration will begin the authorization flow by requesting a device code.
$ curl --request POST --user {key}:{secret} --data {body} https://{hostname}/@app/auth/{authid}/token/device.json
// URL encoded form payload
scope={scope}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {scope} | string | Single space-separated scopes of the authorization request (required: profile) (allowed: profile seated) |
The device code data will be returned in application/json; charset=utf-8 format.
{
"device_code": "{device_code}",
"user_code": "{user_code}",
"verification_uri": "{verification_uri}",
"verification_uri_complete": "{verification_uri_complete}",
"expires_in": {expires},
"interval": {interval}
}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {hostname} | string | The Expert site hostname |
| {authid} | int | The identity provider service to use for authentication |
| {key} | string | The OAuth API Token key |
| {secret} | string | The OAuth API Token secret |
| {device_code} | string | The code that the integration will use to poll for an access token |
| {user_code} | string | The code that the user will provide to the Expert site on a web browser |
| {verification_uri} | URL string | The Expert site URL where the user will provide their code |
| {verification_uri_complete} | URL string | The Expert site URL where the user will provide their code with the code included as a query parameter (NOTE: This is useful for non-textual representations of the URL, such as QR codes if necessary) |
| {expires_in} | int | Seconds until the authorization request expires (default: 3600) |
| {interval} | int | Required seconds between poll attempts (default: 5) |
Example Device Code JSON
{
"device_code": "a722657ed0b1c1bf4d4c099c4b6bbc76fd30ff2c13fdb42d7f33b7394bcb6c7d",
"user_code": "8cde81c",
"verification_uri": "https://example.com/@device/1/2d46b20",
"verification_uri_complete": "https://example.com/@device/1/2d46b20?user_code=8cde81c",
"expires_in": 3600,
"interval": 5
}
It is the responsibility of the integration maintainer/developer to provide the verification URL with clear next steps to the user.
Poll for an Access Token
While the user follows the verification URL to enter the user_code into an awaiting authorization form, the integration or script begins polling the access token endpoint, at the rate of {interval}, until the user completes the flow.
$ curl --request POST --user {key}:{secret} --data {body} https://{hostname}/@app/auth/{authid}/token/access.json
// URL encoded form payload
grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:device_code&device_code={device_code}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {hostname} | string | The Expert site hostname |
| {authid} | int | The identity provider service used for authentication |
| {key} | string | The Trusted Internal API Token key |
| {secret} | string | The Trusted Internal API Token secret |
| {body} | application/x-www-form-urlencoded | The URL encoded access token request payload |
| {device_code} | string | The device code received from the device code request |
Until the user completes the authorization flow, the access token endpoint will respond with the status code 428 Precondition Required.
The authorization form displayed during the Device Code Flow contains a form input labeled "Device Code". This is the field to receive the value of {user_code}.
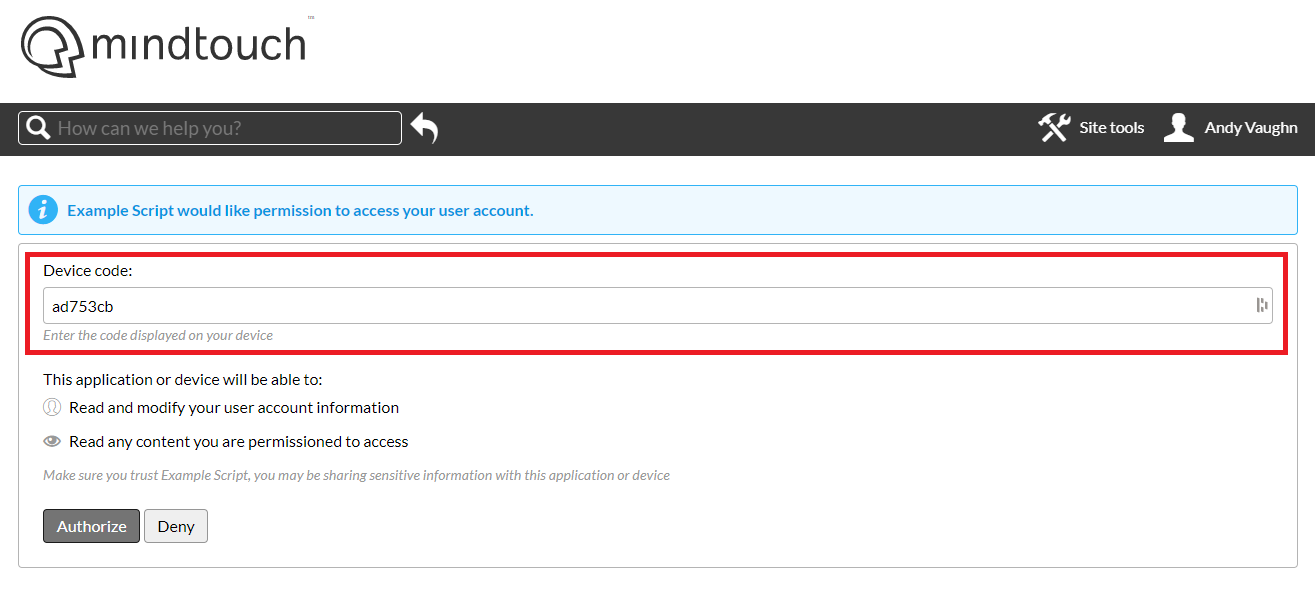
The access token response is common to all authorization flows, and is described in detail later in this article.
Access Token Response
The access token data will be returned in application/json; charset=utf-8 format.
{
"access_token": "{access_token}",
"refresh_token": "{access_token}",
"token_type": "bearer",
"expires_in": "{expires}",
"scope": "{scope}"
}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {access_token} | string | The access token (in Expert Auth Token format) |
| {refresh_token} | string | A refresh token to request a new access token if it expires |
| {expires} | int | The TTL of the access token |
| {scope} | string | The scope of the access token |
Example Access Token JSON
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6ImEzZDFmYWY5YTI0Mzc1ZTFlOTQ1ZjViNGIxMTE0NjNhZGQxY2Y3MDcxMjVkZDMwNTMwMDkzYTU4YjE4NjExYjEiLCJ0eXAiOiJKV1QifQ.eyJhdWQiOiJodHRwczovL2Jhci5taW5kdG91Y2guYmUiLCJleHAiOjE1ODc2MDc3MDgsImlhdCI6MTU4NzYwNDEwOCwic3ViIjoxLCJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL2Jhci5taW5kdG91Y2guYmUvQGFwaS9kZWtpL3NlcnZpY2VzLzEiLCJodHRwczovL21pbmR0b3VjaC5jb20vYXV0aHRva2VuL3NlYXRlZCI6ZmFsc2V9.khUs46bJN2znSsgfc09cdU4eBrpGkDUOe7p0IqQl2gs",
"refresh_token": "1_1587604108_93CE345F6F77E66E7FA5F0E6A69BD1A3D31D938F8F1F19D28996E6CEDD2A976D",
"token_type": "bearer",
"expires_in": "3600",
"scope": "profile"
}
The access token will be used in subsequent requests to the Expert API as a bearer token. A bearer token is the final stage of access validation. The "bearer" of the token effectively has all the rights that the token permits and no further verification is required.
Do not treat bearer tokens in a cavalier manner: secure them as if they were keys to a bank vault.
Bearer tokens are used in Expert API requests by adding them to a Bearer Authorization HTTP header:
$ curl --request GET --header 'Authorization: Bearer {access_token}' https://{hostname}/@api/deki/users/current?dream.out.format=json
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {hostname} | string | The Expert site hostname |
| {access_token} | string | The access token (in Expert Auth Token format) |
Using a Refresh Token to Retrieve a New Access Token
If an access token expires, a refresh token can be used to retrieve a new one (provided that the refresh token itself has not expired).
$ curl --request POST --user {key}:{secret} --data {body} https://{hostname}/@app/auth/{authid}/token/access.json
// URL encoded form payload
grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:device_code&device_code={device_code}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {hostname} | string | The Expert site hostname |
| {authid} | int | The identity provider service used for authentication |
| {key} | string | The OAuth API Token key |
| {secret} | string | The OAuth API Token secret |
| {body} | application/x-www-form-urlencoded | The URL encoded access token request payload |
| {device_code} | string | The device code received from the device code request |
Client-Side Interactions
Client-side interactions aka Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is supported by default with a properly configured Host variable on an OAuth2.0 key/secret creation. Wildcard domains are supported. When using this token, it will respond with Origin headers when implementing the Authorization Code Flow . Upon sending a request with a proper Authorization header provided from an integrator's backend integration with the authtoken value (a signed token in JSON Web Token format). This approach secures access to Expert's API by clients coming from a different origin other then the Expert site. This GitHub example illustrates how a token is passed from a backend to user in the browser to make requests to an Expert service.
Unsupported Integrations
Client-Side Only JavaScript
Pure client-side JavaScript applications, running in a browser, with no server backed application, are presently not supported by this implementation. In the past, OAuth 2.0 allowed public clients (client-side JavaScript, mobile apps, etc) to request an access token using the Implicit Flow. Expert has no plans to implement the Implicit Flow.
In the OAuth ecosystem, due to some inherent security concerns, the Implicit Flow was always considered a stop-gap until a better solution could be devised. That solution is PKCE. However, the Expert OAuth 2.0 system does not yet support this technology.

